
At Huels, our Dimethyl Terephthalate (DMT) production process begins with the oxidation of a mixture of p-xylene and p-toluic acid methyl ester (pT-Ester) in the liquid phase using air and a cobalt-manganese catalyst. This reaction yields p-toluic acid and monomethyl terephthalate.
The resulting mixture, known as the oxidate, is subsequently esterified with methanol to produce the corresponding methyl esters, collectively referred to as raw ester.
The raw ester is then separated by fractional distillation into three streams:
- pT-Ester fraction (recycled to the oxidation stage)
- DMT fraction (purified by crystallization)
- Residue
A portion of the purified DMT is processed in a solid-state unit to prepare it for export.
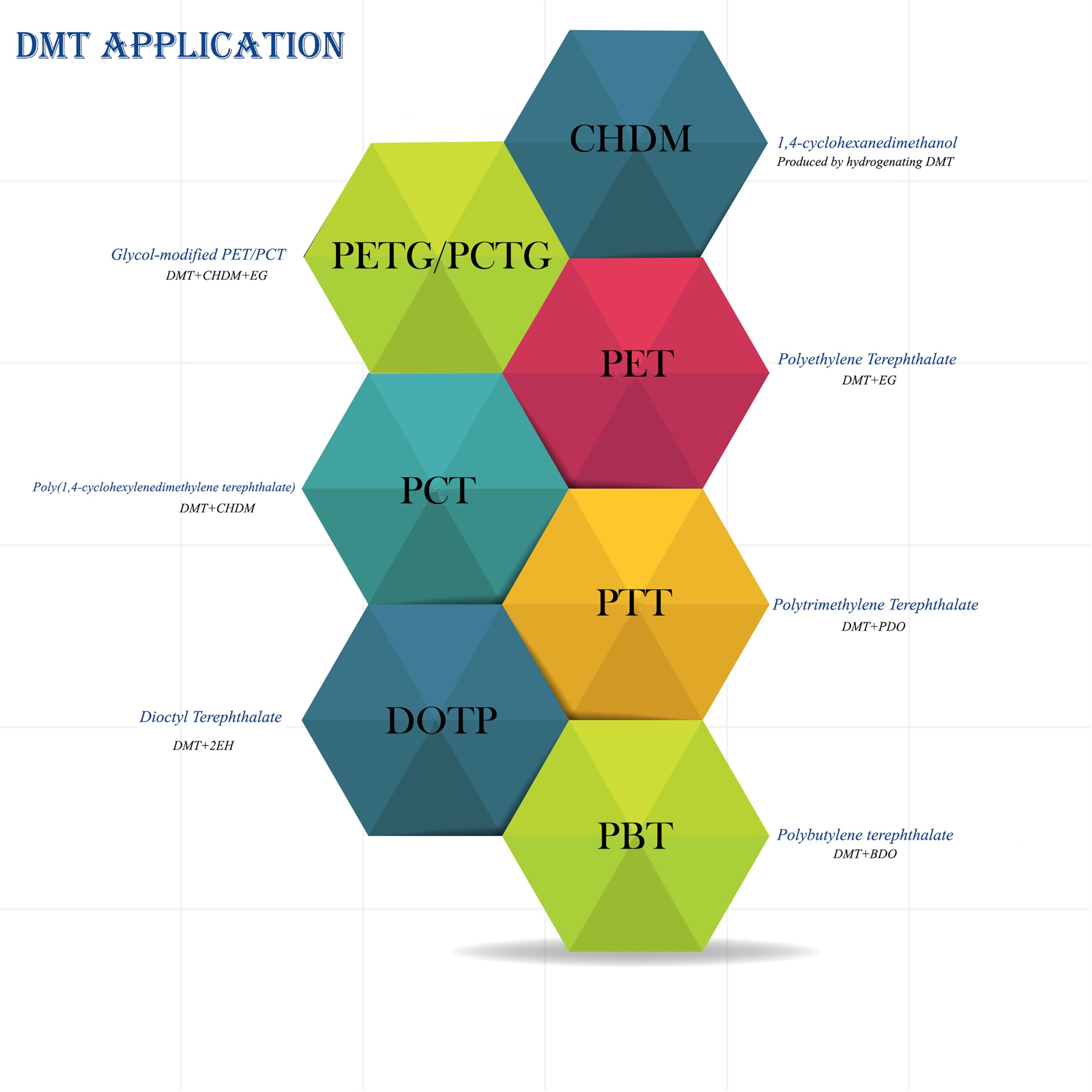
This high-purity product is primarily used in the manufacture of polyester resins, fibers, and films, as well as plasticizers such as DOTP, PBT, and CHDM.

Dioctyl Terephthalate (DOTP) is an organic compound with the chemical formula C₂₄H₃₈O₄. As a non-toxic plasticizer, DOTP exhibits excellent compatibility with polymeric materials, particularly in PVC applications. It is widely used in the production of medical devices, toys, synthetic leather, and other related products. Due to its environmentally friendly characteristics, DOTP has attracted significant attention in the plasticizer industry.
DOTP esters are primarily synthesized through the reaction of Dimethyl Terephthalate (DMT) with 2-Ethylhexanol, under pressurized conditions in the presence of catalyst. In the subsequent stage, the methanol formed during the reaction, along with any excess 2-Ethylhexanol, is removed through a two-step vacuum distillation process. Finally, the resulting product is purified by filtration, yielding high-quality DOTP suitable for various industrial applications.


